In case you want to automate the conversion of Classic or RDLC reports or reconversion of ForNAV reports you might want to use the ForNAV Powershell commandlet “Invoke-ReportsForNavConvert”, which has the same capabilities as the ForNAV converter – but without the user interface
Instead input is given as parameters:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
|
TableDefinitions <path | url> |
Path to NAV table definition, URL to Fields oData webservice or path to App files(s) (use *.app to include all App files in directory) |
|
|
Path <path> |
Path to report .txt source file |
|
|
Destination <path> |
Path to report .txt destination file |
|
|
ConvertRdlcReports <bool> |
Convert RDLC reports to ForNAV reports |
$false |
|
RequestPageOptionCaptionML <string> |
Sets OptionCaptionML for the request page |
ENU=Options |
|
ObjectIdDelta |
Sets a delta which should be added to the object number to avoid overlapping with already existing objects in NAV |
0 |
|
FindReplace <path> |
Path to the ForNAV hint file |
|
|
UseRequestPage <bool> |
If both a request form and a request page is defined for the report true means that the page will be used and false that the form will be used |
$false |
|
NavCompatibility <NavCompatibilitySelection> |
Sets the compatibility of the output objects. Small differences in NAV versions require that you specify the version of NAV, you wish to use with your report objects. Valid values are Nav2013 (use with 2013 and 2013 R2), Nav2015 (use with NAV 2015 and 2016), Nav2017, Nav2018, BCOnPrem and BCCloud. This setting should be used instead of the old Nav2013Compatible shown below. |
BCOnPrem (this changed over time) |
|
Nav2013Compatible <bool> (deprecated) |
Sets if the report should be compatible with NAV 2013/NAV 2013 R2 or newer versions of NAV. This setting is now deprecated. Please use NavCompatibility instead. |
$false |
|
SeparateDestinationFiles <bool> |
Sets if the output should be in one file or separate files per report |
$false |
|
ExportCaptions |
Path to a txt file where all CaptionML strings from the report layouts is exported to. |
|
|
ImportCaptions |
Path to a txt file where CaptionML strings in the report layouts can be updated from. |
|
|
Diff |
Path to the destination for the diff json file |
|
|
Patch |
Path to a json file containing the diffs that will be applied to the reports |
|
|
Baseline |
Path to a .txt file containing the original ForNAV reports to form a basis for the diff |
|
|
CreateTranslationFiles |
If true all multilanguage string are exported into a set of xlf-files |
$false |
|
UseForNavControlNames |
Normally Txt2Al will convert control sourceexpression shorter than 120 chars to a control id reference instead of using the whole string. When this setting is set to true the limit is 30 chars to avoid very long control id’s |
$false |
|
AppendOldId |
Appends the old object id to the objectname if ObjectIDelta <> 0 |
|
|
CreateCrossReferenceInformation |
Adds dummy al code referencing all the fields references in the layout for use with 3-part cross reference tools |
With ForNAV 4.0 the cmdlet also support conversion of txt objects to al OnPrem (dotnet support) or BC cloud (without dotnet support) – the conversion to al is not limited to ForNAV reports – but can be used on text object types (Pages, Tables, Reports, Codeunits,…)
-
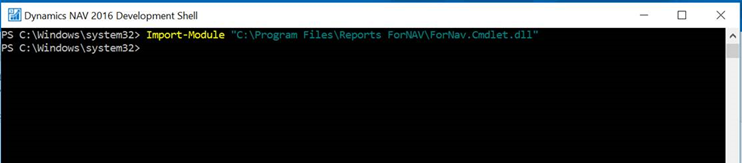
Import the ForNav Commandlet into Powershell
-
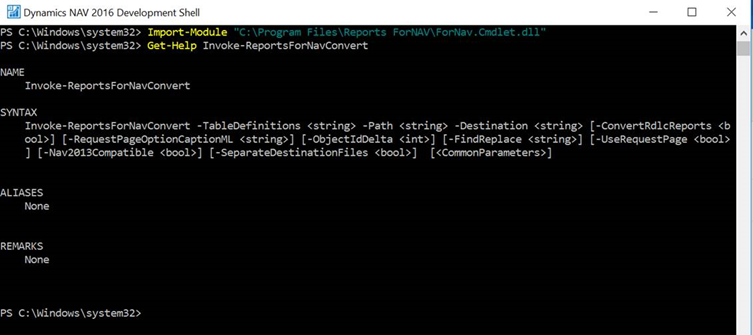
Run the Get-Help command to get an overview of the Invoke-ReportsForNavConvert command
-
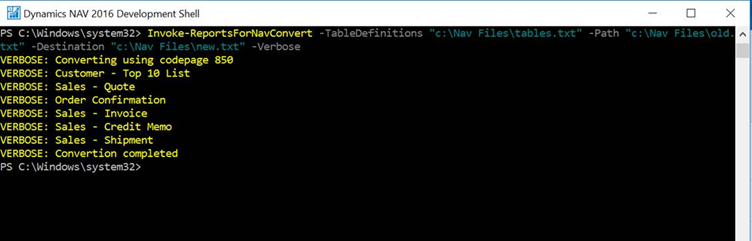
Run the Invoke-ReportsForNavConvert command to do the conversion
Invoke-ExportTranslationFromTxtToExcel -FromTxt <sting> -ToExcel <string> – Exports all multi language strings from al source code to excel
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromTxt |
Source txt file |
|
ToExcel |
Destination excel file |
Invoke-ExportTranslationFromXlfToExcel -FromXlf <string> -ToExcel <string> – Exports all translations from xlf files to excel
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromXlf |
Source xlf file(s) |
|
ToExcel |
Destination excel file |
Invoke-ImportTranslationFromExcelToTxt -FromTxt <string> -FromExcel <string> -ToTxt <string> – creates new al source code with translations based on translations made in Excel
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromTxt |
Source txt file with ENU language strings |
|
FromExcel |
Excel file with translations |
|
ToTxt |
Destination txt file |
Invoke-ImportTranslationFromExcelToXlf -FromXlf <string> -FromExcel <string> -ToXlf <string> – creates new xlf-files based on translations made in Excel
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromXlf |
Xlf file with ENU language strings |
|
FromExcel |
Excel file with translations |
|
ToXlf |
Path to xlf destination files |
Invoke-ExportTranslationFromTxtToJson -FromTxt <sting> -ToJson <string> – Exports all multi language strings from al source code to a json file
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromTxt |
Source txt file |
|
ToJson |
Destination json file |
Invoke-ExportTranslationFromXlfToJson -FromXlf <string> -ToJson <string> – Exports all translations from xlf files to json
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromXlf |
Source xlf file(s) |
|
ToJson |
Destination json file |
Invoke-ImportTranslationFromJsonToTxt -FromTxt <string> -FromJson <string> -ToTxt <string> – creates new al source code with translations based on translations made in a json file
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromTxt |
Source txt file with ENU language strings |
|
FromJson |
Json file with translations |
|
ToTxt |
Destination txt file |
Invoke-ImportTranslationFromJsonToXlf -FromXlf <string> -FromJson <string> -ToXlf <string> – creates new xlf-files based on translations made in a json file
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
FromXlf |
Xlf file with ENU language strings |
|
FromJson |
Json file with translations |
|
ToXlf |
Path to xlf destination files |

